
The synergy between MA元-101 and proteasome inhibition on MM cell growth was then studied in vivo using the xenograft plasmacytoma mouse model. Moreover, strong synergy was found in the in vitro cytotoxic effects of MA元-101 with inhibitors of the proteasome and Hsp90. MA元-101-induced inhibition of MM cell growth was characterized by an arrest of cell cycle progression and activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in these cells. In accordance with our premise, we discovered that MA元-101 exhibits potent inhibitory effects on proliferation and survival of MM cells, including primary tumor cells and EPCs obtained from MM patients. Thus, we reasoned that MA元-101 might act synergistically and potentiate in vitro and in vivo the antimyeloma effects of proteasome and Hsp90 inhibitors. In turn, inhibition of Hsp72 by small molecule inhibitors was shown to potentiate the in vitro apoptotic effects of 17-AAG on MM tumor cell lines. Notably, Hsp70 acts at several nodes in the apoptotic pathway, and thus its inhibition may overcome the differential responsiveness to bortezomib as well as the side effects encountered in its use against MM. Hsp70 gene and protein expression are upregulated in MM cells after exposure to bortezomib as well as after application of 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin (17-AAG), which inhibits Hsp90 chaperones. Fourth, inhibition of Hsp70 in cancer cells triggers tumor-specific apoptosis and cell death by inhibiting lysosomal membrane permeabilization, a hallmark of stress-induced cell death The latter mechanism was suggested by stabilization of lysosomes via Hsp 70 binding to an endolysosomal anionic phospholipid bis(monoacylglycero)phosphate (BMP), an essential cofactor for lysosomal membrane sphingomyelin metabolism. Third, Hsp70 gene expression and overexpression are associated with human cancers. Second, Hsp70 expression is upregulated in MM cells, and in treatment-resistant MM cell lines, and especially after exposure to clinically effective antimyeloma drugs that inhibit other components of the protein quality control machinery. First, in plasma cells, the Hsp70 homolog in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), BiP, enhances the folding and secretion of normal and misassembled immunoglobulins (IGs) and prevents their accumulation. Our rationale for studying the antimyeloma effects of MA元-101 was fourfold. MA元-101 inhibits the ability of Hsp40 cochaperones to stimulate Hsp70 ATPase activity and thereby compromises essential Hsp70 cellular functions. Thus, blockade of molecular chaperones is currently being explored in preclinical studies and clinical trials for their antimyeloma effects, either synergistic with bortezomib or in combination with other agents. The potent antimyeloma effects of bortezomib (PS-341 Velcade), a first-in-class selective inhibitor of the 26S proteasome, are largely due to a cellular stress response characterized by transcription of proteasome subunits and molecular chaperones of the heat shock protein family which include Hsp90 and Hsp70, and their downstream regulators of tumor growth. However, both the tumor and microenvironment in MM are significantly affected by proteasome inhibition via interruption of cell survival pathways.

Equally important in MM pathogenesis and progression are the tumor enhancing effects of the BM microenvironment, particularly the increased neovascularization of the MM niche by endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). Despite significant improvements in patient outcomes as a result of high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell rescue, and novel therapies with bortezomib, thalidomide, and lenalidomide, disease progression in MM leads to mortality resulting from accumulating genetic mutations, prolonged tumor survival, and treatment resistance. MM is a bone marrow (BM) neoplasm of plasma cells and remains incurable. This study explored the cytotoxic effects of MA元-101, a recently developed inhibitor of Hsp70, on multiple myeloma (MM) tumor growth. Small molecule inhibition of Hsp70 function,Įither alone or in combination with otherĪgents, as an effective therapeutic strategy for These data support a preclinical rationale for
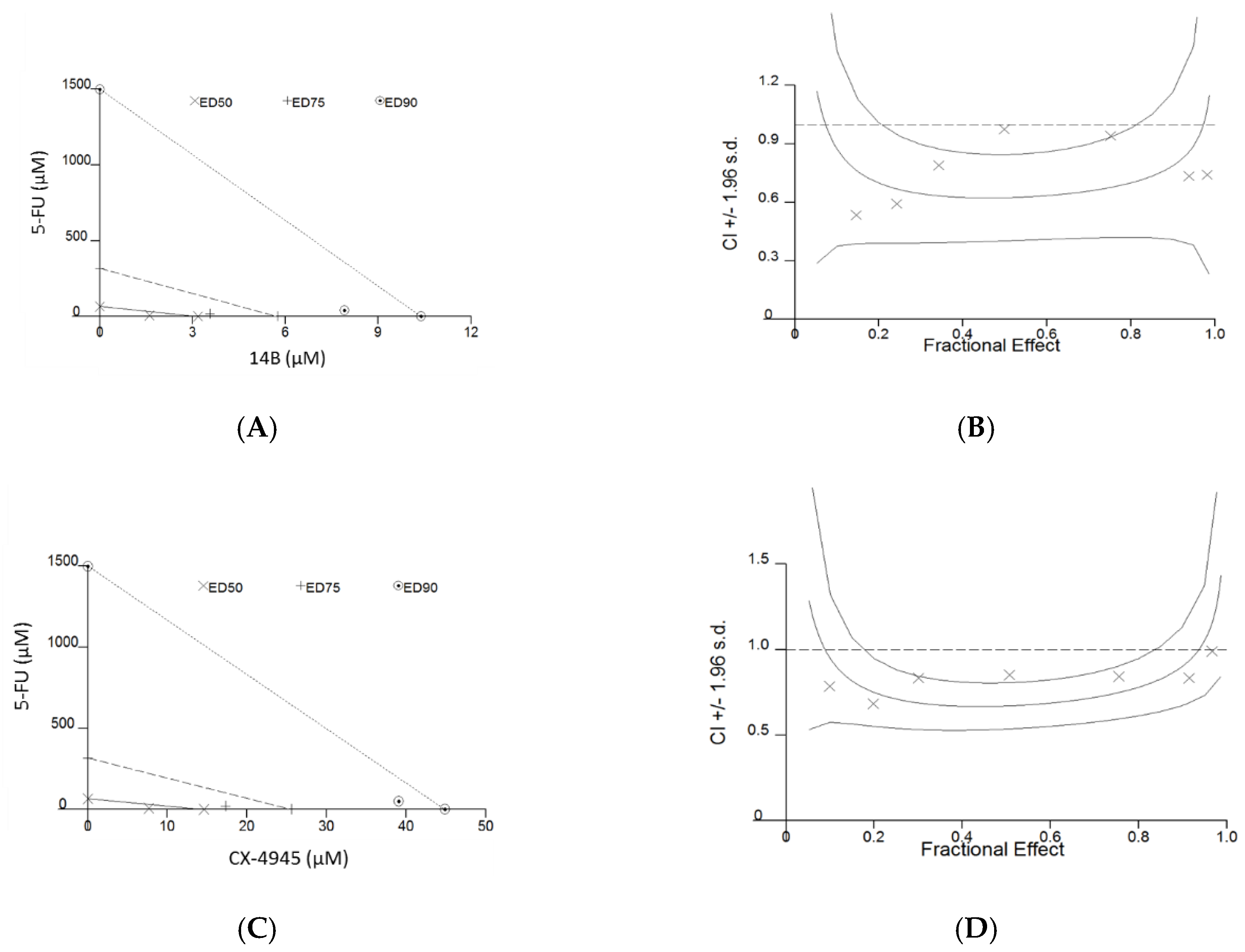
In combination withĪ proteasome inhibitor, MA元-101 significantly Primary tumor cells and bone marrow endothelialĬells from myeloma patients. Xenograft plasmacytoma model, as well as on Non-ATP-site inhibitors of the heat shockĭiscovered that MA元-101 exhibited antimyeloma Toward this goal, we examined the antimyelomaĮffects of MA元-101, a member of a new class of Targeting new and nonredundant pathways in MM. That act synergistically with existing effectiveĬoncentrations, avoid treatment resistance, and To the treatment-refractory/resistant nature ofĬompelling challenge is to develop new drugs
Malignancy and remains incurable, primarily due

(MM) is the second most common hematologic


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
